29 U.S. Loneliness Statistics & Facts: Are People Lonely?
Did you know that 52% of Americans report feeling lonely? Find more scary loneliness statistics in this roundup.
Key Loneliness Statistics & Facts
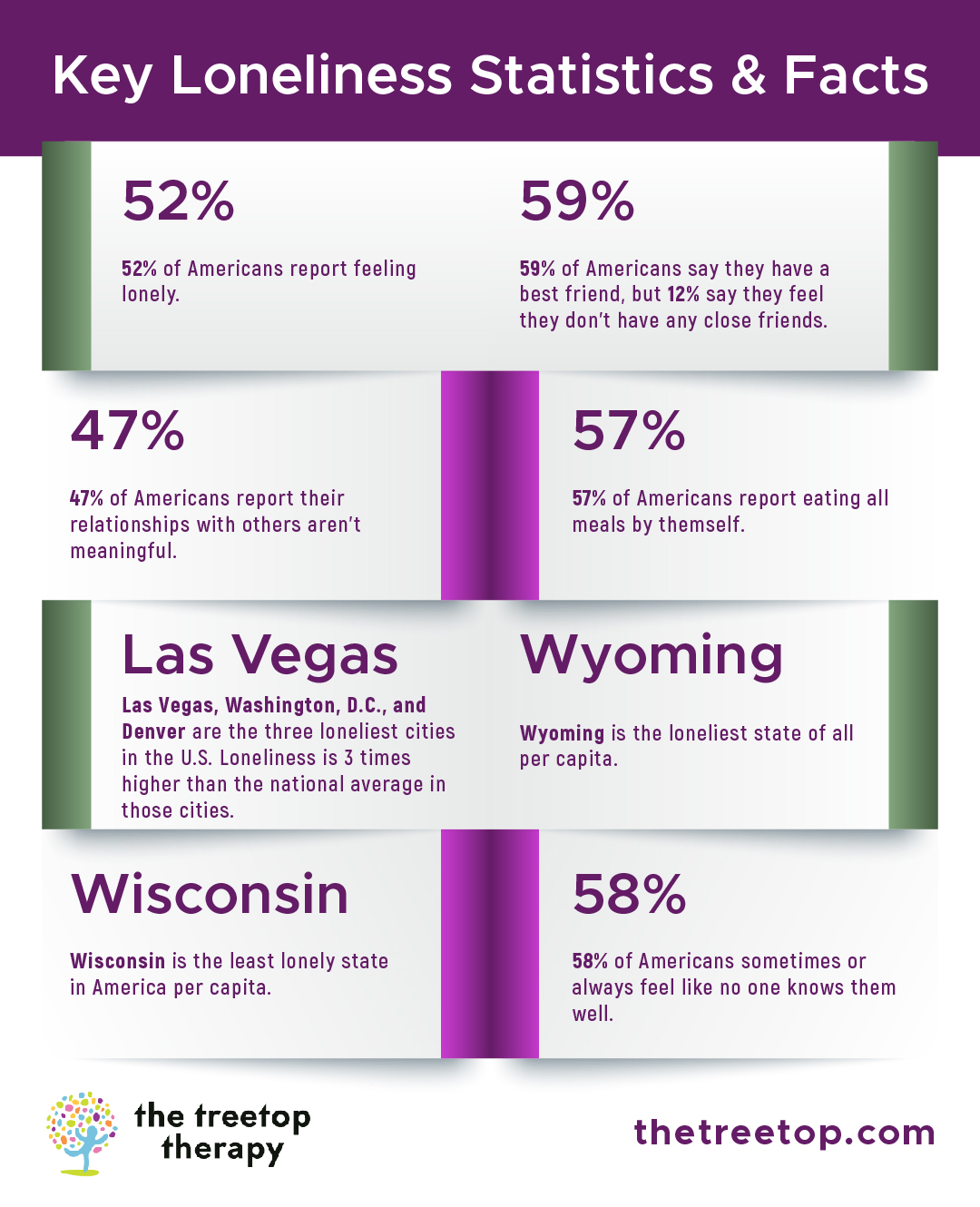
- 52% of Americans report feeling lonely.
- 59% of Americans say they have a best friend, but 12% say they feel they don't have any close friends.
- 47% of Americans report their relationships with others aren't meaningful.
- 57% of Americans report eating all meals by themself.
- Las Vegas, Washington, D.C., and Denver are the three loneliest cities in the U.S. Loneliness is 3 times higher than the national average in those cities.
- Wyoming is the loneliest state of all per capita.
- Wisconsin is the least lonely state in America per capita.
- 58% of Americans sometimes or always feel like no one knows them well.

Loneliness Statistics: A Growing Concern
Loneliness is a universal human experience, but it has become an increasingly prevalent problem in modern society.
With the rise of social media and the decline of face-to-face interactions, people are feeling more isolated than ever before. In this article, we'll explore the latest loneliness statistics and what they mean for individuals and society as a whole.

How Many People Are Lonely?
According to a recent survey conducted by the Kaiser Family Foundation, 22% of adults in the United States say they often or always feel lonely or isolated. That's more than one in five people who are struggling with loneliness on a regular basis.

The same study found that younger generations report feeling more lonely than older generations, with 25% of adults aged 18-29 reporting feelings of loneliness compared to only 9% of those aged 65 and older.
These statistics are alarming and suggest that loneliness is not only a prevalent problem but also one that may be increasing over time.
The Prevalence Of Loneliness
According to a recent survey by Cigna, nearly half of all Americans report feeling lonely.

This is a startling statistic, especially when you consider that loneliness has been linked to a host of negative health outcomes, including depression, anxiety, and even premature death. In fact, some studies have suggested that loneliness is as harmful to our health as smoking or obesity.
Loneliness Demographics
Loneliness does not discriminate, but it affects different groups of people in different ways. According to a study by the AARP Foundation, older adults are more likely to experience chronic loneliness than any other age group.

The study found that 42% of older adults experience loneliness on a regular basis, which can have serious health consequences for this vulnerable population.
In addition to age, gender is another factor that influences loneliness.
Women are more likely than men to report feeling lonely or isolated, according to a study published in the Journal of Women's Health. The study found that women who were divorced or widowed were at an even higher risk of experiencing loneliness.
Race and ethnicity also play a role in loneliness. Research has shown that African Americans and Hispanic Americans are more likely than white Americans to report feeling lonely or socially isolated. This may be due in part to factors such as discrimination and social inequality.
Understanding the demographics of loneliness can help us develop targeted interventions and support systems for those who are most at risk. It's important for individuals, communities, and policymakers alike to recognize the scope of this issue and work together to address it effectively.
Loneliness and Social Media Statistics
One of the main drivers of loneliness in modern society is social media. While social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram are designed to connect people, they can actually have the opposite effect.

Studies have shown that people who spend more time on social media are more likely to feel lonely and isolated. This is because social media often creates a distorted view of reality, where people only share their best moments and hide their struggles and difficulties.
What Percent Of People Are Lonely?
Loneliness is not evenly distributed across age groups. According to a study by the Kaiser Family Foundation, young adults are the most likely to report feeling lonely, with 48% of those aged 18-29 saying they often feel lonely.
This is in contrast to older adults, who are generally less likely to feel lonely. However, this may be changing as the baby boomer generation ages and experiences more social isolation.
The Importance Of Connection
Loneliness is a complex problem with no easy solutions. However, one thing is clear: connection is key. Whether it's through in-person interactions, phone calls, or video chats, staying connected with others is essential for our mental and physical well-being.
As a society, we need to prioritize connection and find ways to combat the growing problem of loneliness.
In conclusion, loneliness is a serious problem that affects millions of people around the world. By understanding the latest loneliness statistics and the factors that contribute to this problem, we can work together to create a more connected and supportive society.
Loneliness Facts & Statistics
Loneliness can have a profound impact on mental health, leading to a range of negative outcomes. Research has shown that people who experience chronic loneliness are at increased risk for depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders.
In fact, one study found that lonely individuals were twice as likely to develop depression than those who were not lonely.
Loneliness is also linked to increased stress levels and decreased resilience in the face of stressors. This is because social support plays an important role in helping people cope with stress and adversity.
Without adequate social support, individuals may struggle to manage the challenges of daily life.
Another way that loneliness can impact mental health is through its effect on self-esteem. When people feel isolated or excluded from social groups, they may begin to question their own worth and value as individuals. This can lead to feelings of low self-esteem and even contribute to the development of personality disorders.
Overall, the impact of loneliness on mental health is significant and cannot be ignored. As a society, we need to prioritize efforts to reduce loneliness and increase social connection in order to promote better mental health outcomes for all individuals.
The Physical Health Consequences of Chronic Loneliness
In addition to the negative impact on mental health, chronic loneliness can also have serious physical health consequences.
A study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that people who experienced social isolation and loneliness were at a higher risk for early mortality than those who had strong social connections.
One reason for this increased risk is that chronic loneliness has been linked to a weakened immune system.
When we experience social isolation, our bodies produce more stress hormones like cortisol, which can suppress the immune system over time. This makes us more vulnerable to infections and illnesses.
Furthermore, chronic loneliness can also increase inflammation in the body, which is associated with a range of health problems including heart disease and diabetes. Inflammation occurs when the body's immune response goes into overdrive, leading to damage to healthy tissues and organs.
Finally, chronic loneliness has been shown to have an impact on sleep quality. People who feel socially isolated or lonely are more likely to experience disrupted sleep patterns, which in turn can lead to a host of other health problems such as obesity and cardiovascular disease.
Overall, the physical health consequences of chronic loneliness are significant and cannot be ignored. It's important for individuals who are experiencing feelings of social isolation or loneliness to seek out support from friends, family members or healthcare professionals in order to mitigate these negative effects on both their mental and physical well-being.






